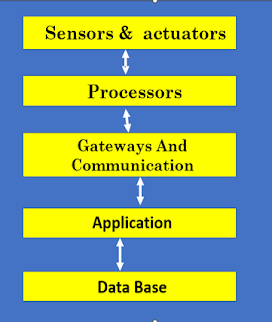
Building blocks of IoT
Five basic building blocks of the IoT system –sensors, processors, gateways, applications, and database.
1.Sensors & Actuators:
- The front end of the IoT devices. These are the so-called “Things” of the system.
- The main purpose is to collect data from its surroundings (sensors) or give out data to its surrounding (actuators).
- Uniquely identifiable devices with a unique IP address so that they can be easily identifiable over a large network.
- Able to collect real-time data. These can either be autonomous in nature or user-controlled.
- Examples of sensors are gas sensors, water quality sensors, moisture sensors, etc.
Actuators
- · Both sensors and actuators are transducers, which means they’re responsible for converting signals from one form to another.
- · Actuators are responsible for performing actions.
- Sensors and actuators work together to remotely monitor and control physical processes
- or systems.
- Sensors and actuators are only endpoints that connect physically to the environment, whereas analysis of the information they collect actions in a control layer, is referred to as an IoT gateway.
2. Processors:
- ·
Processors are the
brain of the IoT system.
- ·
Processors are
primarily real-time devices that can be readily manipulated by software.
- ·
These are also in
charge of data security, which includes data encryption and decryption.
- · the Main function is
to process the data captured by the sensors.
- ·
Extract the
valuable data from the huge amount of raw data collected (intelligence to the
data).
- ·
Processors mostly
work on a real-time basis and are easily controlled by applications.
- ·
Also responsible
for securing the data – perform encryption and decryption of data.
- ·
Embedded hardware
devices, microcontrollers, etc process the data
Electronic Conversion:
o
An analog to
digital converter (ADC) on a printed circuit board (PCB) translates information
from the pressure sensor into a format that can be digitally transmitted.
o
Without diving
into the details, in this example the pressure sensor has a signal output of 4
volts which the ADC recognizes as the integer number 40, which corresponds to a
value of 40 psi, which is then represented in binary form as 101000 (machine
language).
Transmission:
o
The binary value
captured from the sensor is encrypted for security reasons (or should be) and
is sent from the on-site computer network via the Internet to a remote cloud
computing or data center.
o
Data transmission
most often takes place at regular time intervals based on the application
needs, or sometimes only when there is a significant change in the sensor’s
value.
3. Gateways:
·
Gateway is a
device that’s used for the basic analysis of data coming from connected sensors.
·
Gateways are
responsible for routing the processed data and sending it to proper locations for
its (data) proper utilization.
·
Work as decision points, sending
certain control commands to actuators which, in turn, perform appropriate
actions.
·
Gateway helps in
to and from the communication of the data.
·
It provides
network connectivity to the data.
·
Network
connectivity is essential for any IoT system to communicate.
·
Lan, wan, pan, etc
are examples of network gateways.
·
Both
microcomputers and microprocessors can be used as gateways for IoT applications.
4. Applications:
·
Applications are
essential for proper utilization of all the collected data.
·
These are cloud-based.
·
Responsible for
rendering the effective meaning to the data collected. Applications are
controlled by users and are a delivery point of particular services.
·
Examples of
applications are home automation apps, security systems, industrial control
hubs, etc.
5. Data Storage:
·
After reaching its
final destination, the sensor value is typically stored in a computer database
that can easily serve other systems (hence the name “server”).
·
Datastore on the server which may be either local or cloud and both.
==============================



0 Comments